Notebooks
Premium
Trends
BioTuring
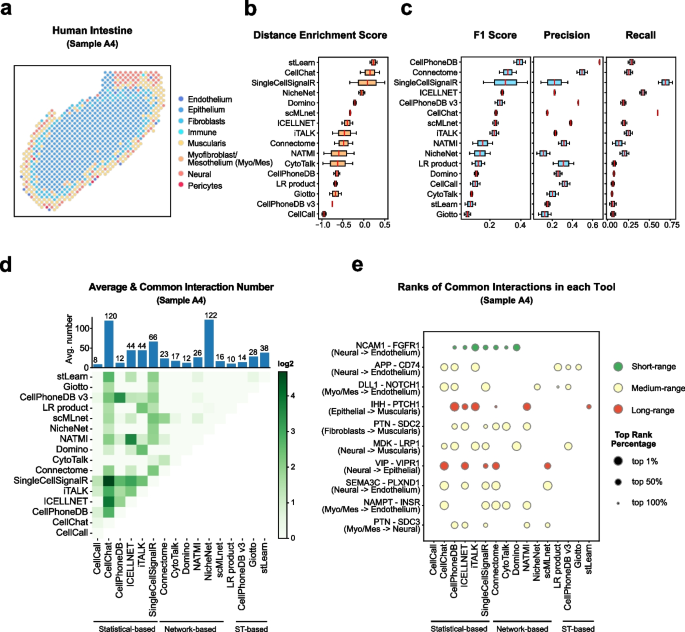
Cell–cell communication mediated by ligand–receptor complexes is critical to coordinating diverse biological processes, such as development, differentiation and inflammation.
To investigate how the context-dependent crosstalk of different cel(More)